Vp Shunt Programmable Vs Non Programmable

Fixed or chronology.
Vp shunt programmable vs non programmable. In 33 of 57 patients with programmable shunts adjustments were made. Stereotactic valve type programmable vs. Programmable valves associated with reduced risk of both overall shunt revision 35 vs 54 p 0 016 and proximal obstruction 12 vs 28 p 0 006.
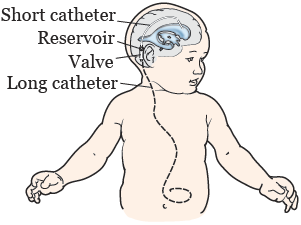
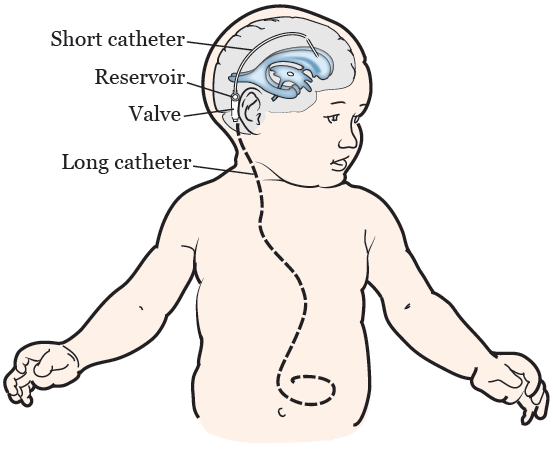
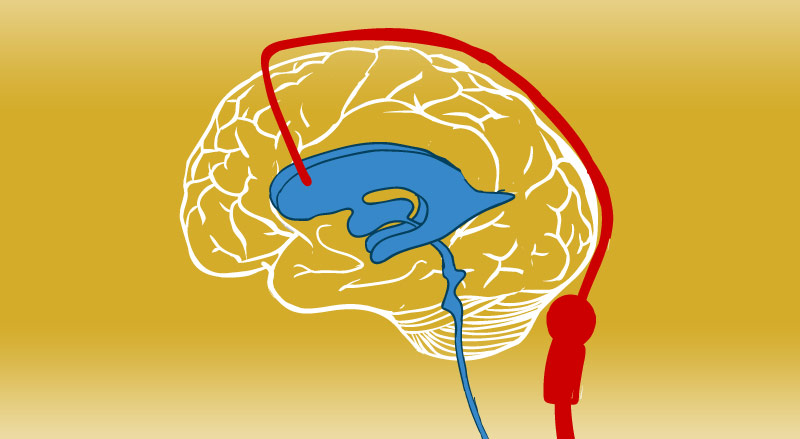
Complication rates following shunt procedures vary from 4 to 85 according to the shunt type vp vs. Influence of etiology and programmable shunts on revisions. Share on pinterest a ventriculoperitoneal shunt is either programmable or nonprogrammable.
The amount of csf your vp shunt drains depends on its pressure setting. Notarianni et al 2009. The purpose of a ventriculoperitoneal shunt is to remove excess fluid from a person s brain.
About your nonprogrammable vp shunt settings. With a nonprogrammable vp shunt your neurosurgeon will choose the pressure setting before the shunt is placed. Four 7 of 57 patients with programmable devices underwent shunt revision whereas 8 21 6 of 37 patients with nonprogrammable shunts underwent shunt revision p 0 0413 and 4 of these patients had programmable shunts inserted during shunt revision.
It seems after reading another thread that people have to frequently adjust the programmable ones while i do nothing to maintain mine. Lp procedure freehand vs. I came to this site after seeing a news piece on programmable shunts on tv.