Pvc Ecg Changes

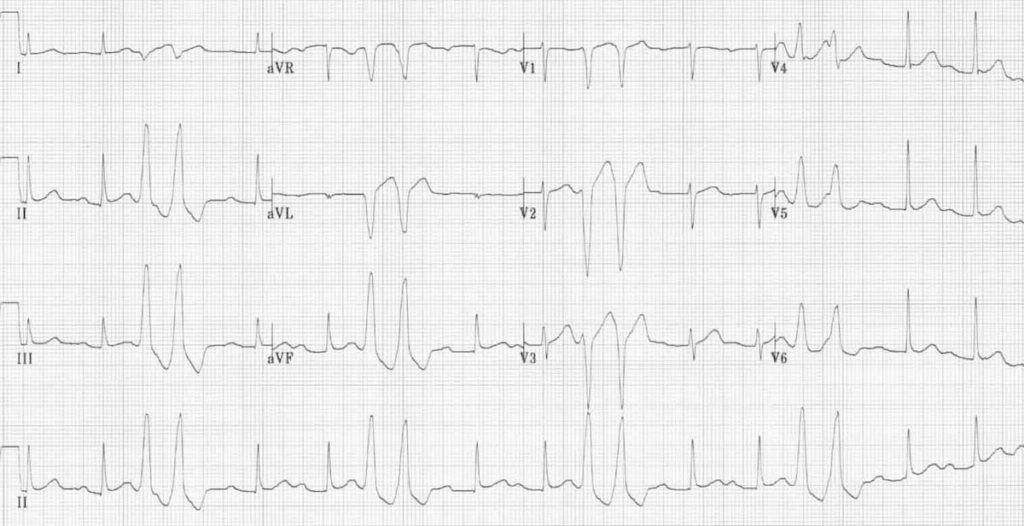
The electrical events of the heart detected by the electrocardiogram allow a pvc to be easily distinguished from a normal heart beat.
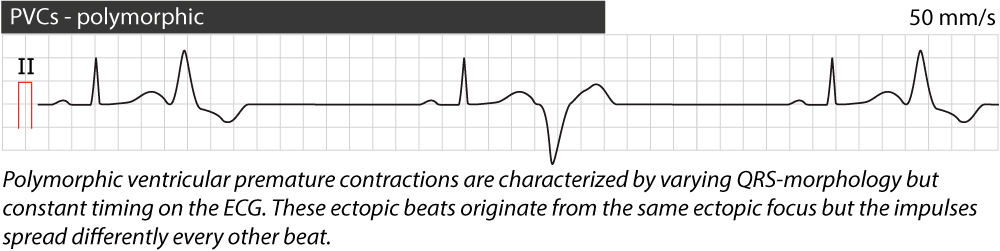
Pvc ecg changes. Even if you ve never had symptoms you may be diagnosed with pvcs during a routine heart test called an electrocardiogram ecg. Grade 1 occasional 30 per hour. Premature ventricular contraction ekg examples grading of frequency.
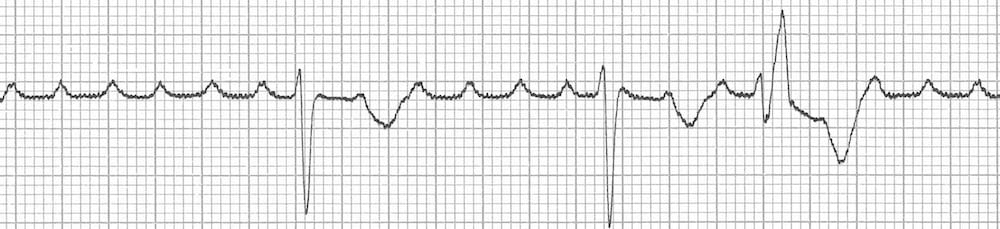
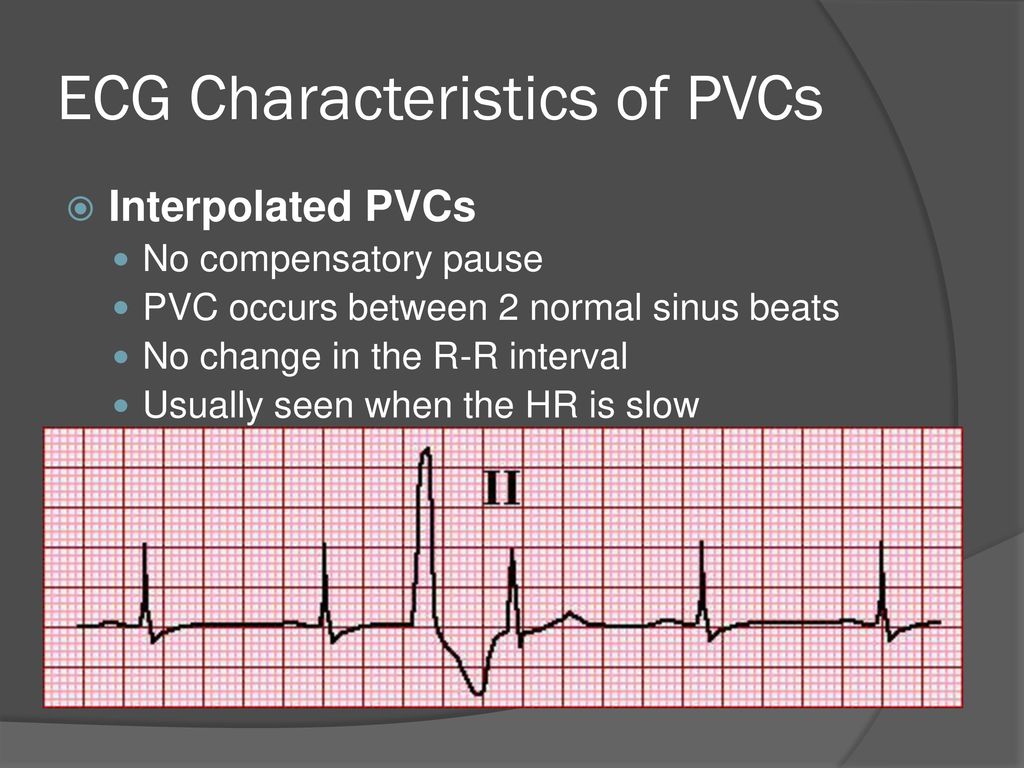
This is called an interpolated pvc and it appears on the ecg as a pvc occurring between two sinus beats and there are no beats. If a pvc occurs early after a normal beat the atrioventricular conduction system might have repolarized by the time the next sinus impulse is discharged this impulse is usually not conducted to the ventricles due to refractoriness in the atrioventricular conduction system whereby the atrial impulse will reach the ventricles and depolarize them. Lown and graboys proposed the following grading system which is used for prognostic purposes.
If pvcs are frequent or. The ecg changes associated with acute pulmonary embolism may be seen in any condition that causes acute pulmonary hypertension including hypoxia causing pulmonary hypoxic vasoconstriction. Pvcs are a normal electrophysiological phenomenon not usually requiring investigation or treatment.
Ultrasound of the heart is therefore recommended in people with pvcs. Key ecg findings include. However very frequent pvcs can be symptomatic of an underlying heart condition.
Seen in 44 of patients. Ischaemic heart disease wpw a pvc may trigger the onset of a re entrant tachydysrhythmia e g. Grade 0 no pvcs.
Furthermore very frequent pvcs are considered a risk factor for arrhythmia induced cardiomyopathy in which the heart muscle becomes less effective and symptoms of heart failure may develop. Sinus tachycardia the most common abnormality. In patients with underlying predispositions e g.