What Is A Vpn Site

A site to site vpn tunnel encrypts traffic at one end and sends it to the other site over the public internet where it is decrypted and routed on to its destination.
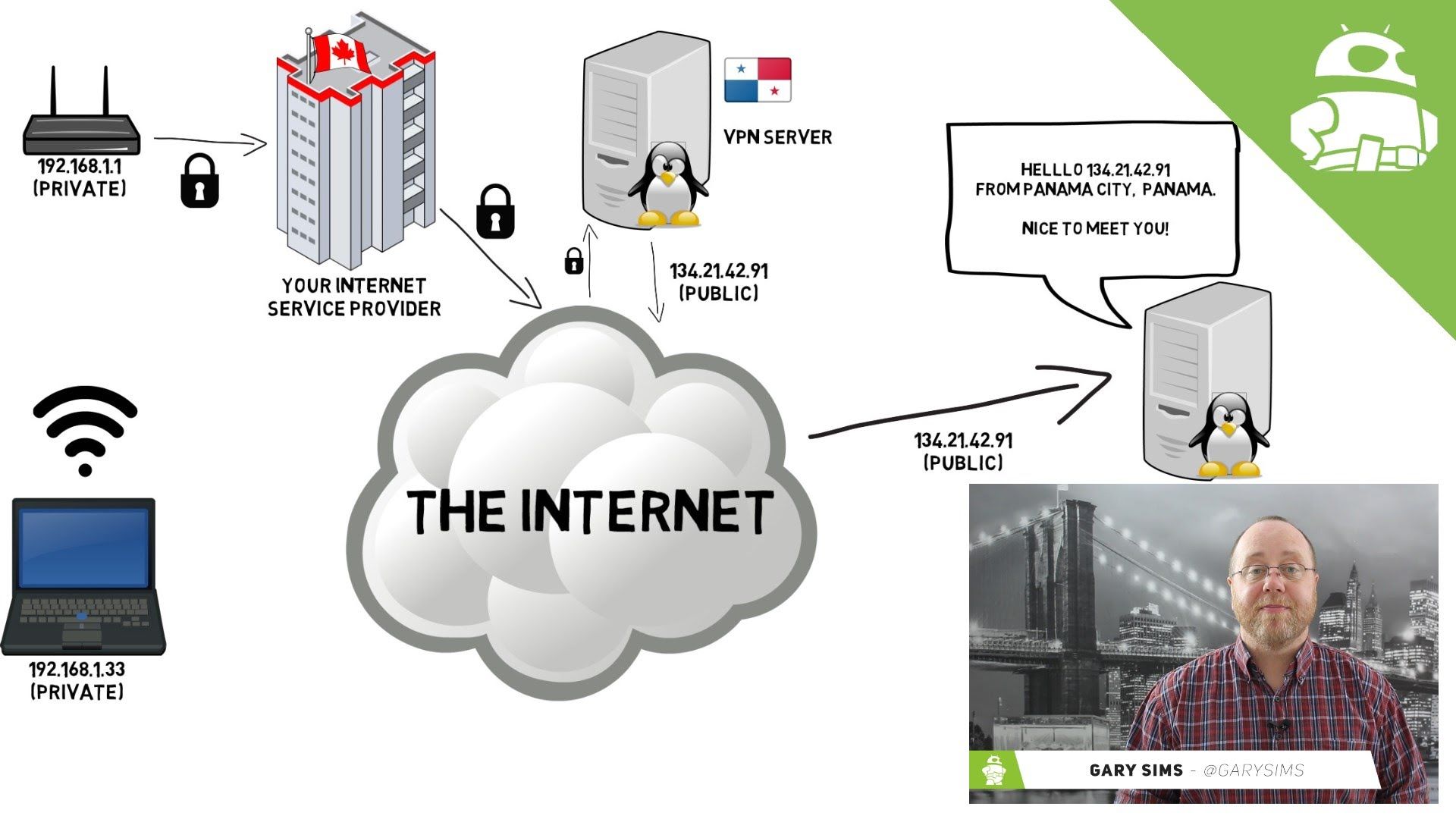
What is a vpn site. This private communication takes place by encrypting the traffic between the gateways of two sites using ciphers and encryption algorithms. Site to site vpn also called as the gateway vpn primarily focuses on communicating privately between two intended sites. Your pc and the vpn server.
It s kind of like a special tunnel on the internet that can hide any data you send or receive. First of all a site to site vpn creates a network to network vpn as opposed to a pc to server one. These days vpns are really popular but not for the reasons they were originally created.
Vpns can be used to access region restricted websites shield your browsing activity from prying eyes on public wi fi and more. Many organizations use site to site vpns to leverage an internet connection for private traffic as an alternative to using private mpls circuits. A vpn or virtual private network allows you to create a secure connection to another network over the internet.
Vpn stands for virtual private network. Applications running across a vpn may therefore benefit from the functionality security and management of the private network. A site to site virtual private network vpn is a connection between two or more networks such as a corporate network and a branch office network.
It provides the ability to connect geographically separate locations or networks usually over the public internet connection or a wan connection. A site to site virtual private network vpn provides this by creating an encrypted link between vpn gateways located at each of these sites. For example if you already have a vpn service to encrypt your traffic installed on your pc the tunnel terminates at two points.
This keeps your information private from your internet service. A virtual private network vpn extends a private network across a public network and enables users to send and receive data across shared or public networks as if their computing devices were directly connected to the private network.