Vp Shunt Overdrainage

The shunt can also become blocked at the distal end if the shunt is pulled out of the abdominal cavity in the case of vp shunts or from similar protein buildup.
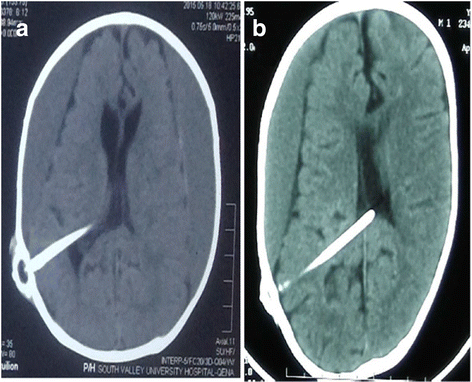
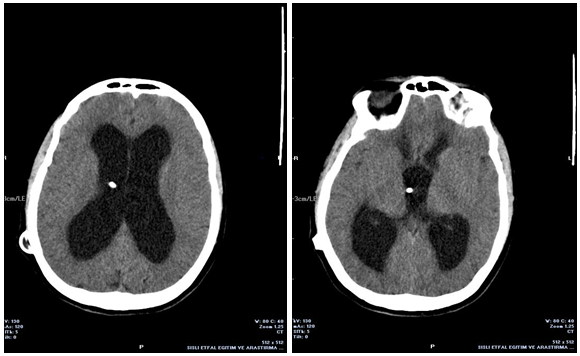
Vp shunt overdrainage. Shunt overdrainage an important complication of shunt surgery is overdrainage which often can be treated with adjustable pressure valve manipulations but also may result in the need for subdural hematoma evacuation. Other causes of blockage are overdrainage and slit ventricle syndrome. The incidence of ventriculoperitoneal shunt failure ranges from 25 to 40 at 1 year and 63 to 70 at 10 years failure rates with ventriculoatrial and ventriculopleural shunts are slightly higher patient presentation varies depending on patient age as well as the cause and acuity of failure symptoms with the highest positive predictive value include nausea and vomiting and decreased.
Patients at higher risk for. Overdrainage is a complication of ventriculoperitoneal shunt but adjustable valves and anti siphon devices can prevent it. These very expensive valves are most often inaccessible so that the majority of the valves available in togo are fixed differential pressure valves.
Shunt patency study assess proximal catheter patency by aspirating 0 5 cc csf occlude distal catheter inject radio isotope flush with appropriate csf image for 20 minutes. Ct head necessary for shunt placement workup and over drained ventricles. Shunt overdrainage represents an incompletely understood condition of variable clinical presentations and imaging findings that still represents a challenge for neurosurgeons in.
Avoiding overdrainage of csf seems an obvious goal in the long term treatment of hydrocephalus. Csf overdrainage in lp shunts. Ambulate and image 2 hours later if no flow.
Shunt overdrainage is a condition with various clinical presentations ranging from mild to very severe symptoms often requiring multiple evaluations and admission in some cases. The csf overdrainage occurs almost exclusively when hydro cephalus patients are treated with ventricular shunts. The condition typically presents with postural headache as well as nausea emesis and irritability exacerbated in an upright position and alleviated in a supine position.