Vp Shunt Mechanism

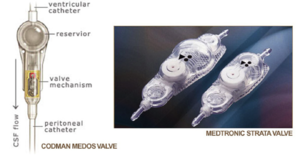
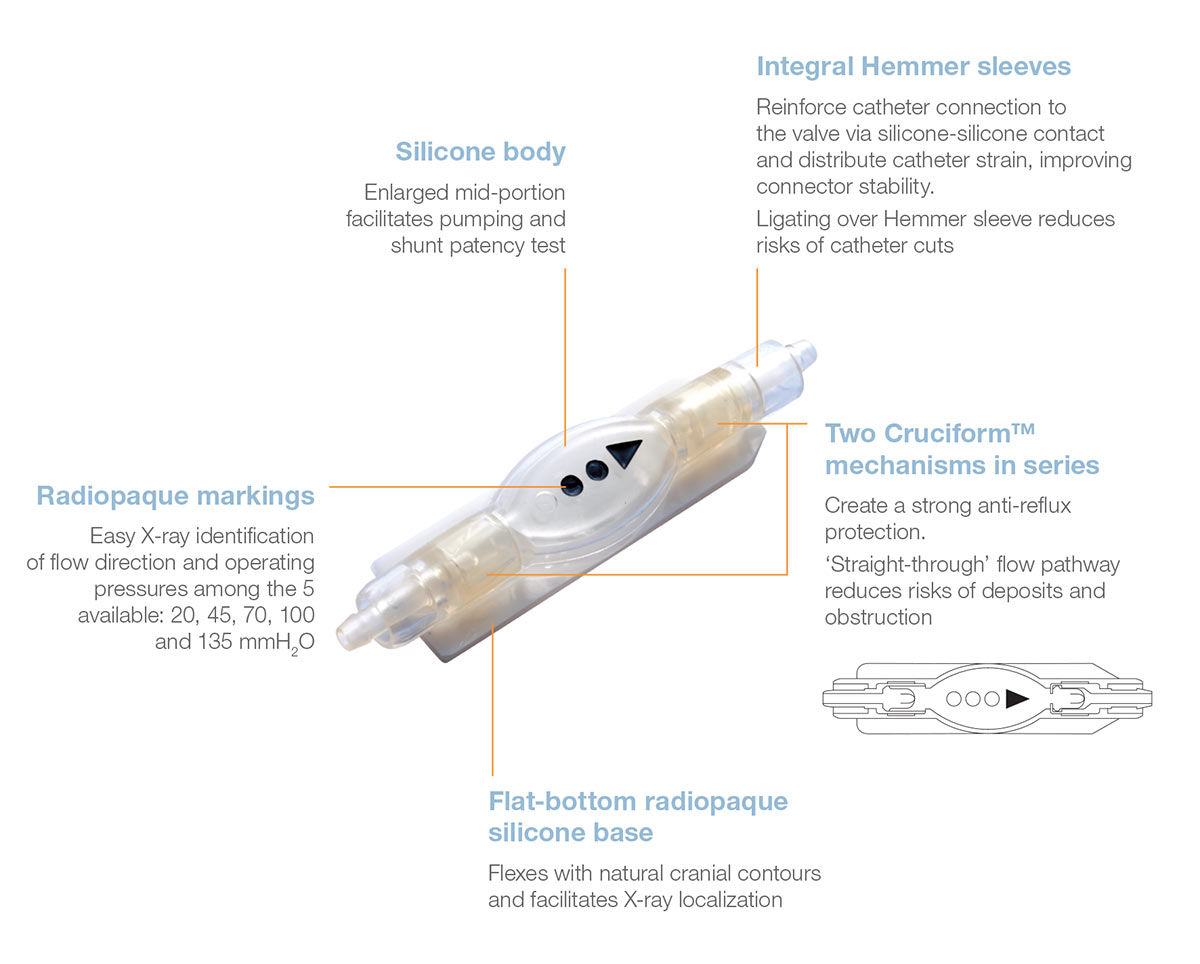
A valve mechanism which regulates differential pressure or controls flow through the shunt tubing.
Vp shunt mechanism. 1 bacterial contamination at the time of surgery. A better understanding of mechanisms of shunt failure will cause an. What is a ventriculoperitoneal shunt.
The diagnosis of shunt failure can be confounded by a variety of factors mechanical failure being the most common cause of multiple shunt revisions in a lifetime. 3 hematogenous spread of infection from another site. A ventriculoperitoneal vp shunt is a medical device that relieves pressure on the brain caused by fluid accumulation.
A vp shunt is used to treat a condition called hydrocephalus. The extra protein will collect at the point of drainage and slowly clog the valve. Vp shunting is a surgical procedure.
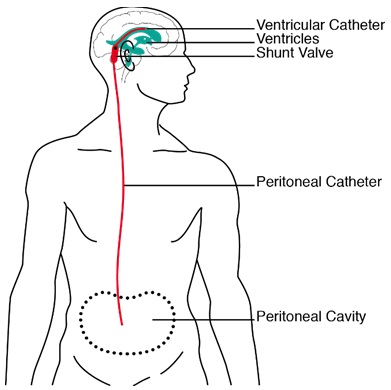
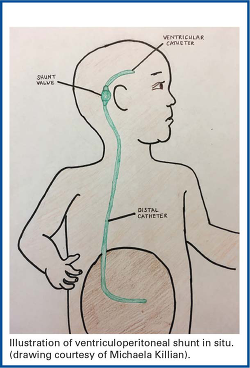
Ventriculoperitoneal vp shunts which are used to treat hydrocephalus shunt cerebrospinal fluid csf from the lateral ventricles of the brain into the peritoneum. 46 this mechanism by which overdrainage is prevented is similar to the mechanism by which a flow regulated valve prevents overdrainage. Diameter of tubing and a longer length of tubing may act as a flow controlled system that prevents overdrainage.
Va and vpl used rarely unless vp contraindicated. Vp shunt also known as a ventriculoperitoneal shunt is a type of medical device that is used to relieve pressure on the brain that builds up from fluid accumulation. And 4 ascending infection from the distal catheter tip kaufman et al 1990.
Proposed mechanisms of intracardiac migration include unintentional transvenous placement of the shunt 29 30 and suction of the catheter into the heart by negative inspiratory pressures. The shunt can also become blocked at the distal end if the shunt is pulled out of the abdominal cavity in the case of vp shunts or from similar protein buildup. Tapping or aspirating the.