Vp Shunt Hearing Loss

This study is aimed to show the relationship between vp shunt and hearing loss.
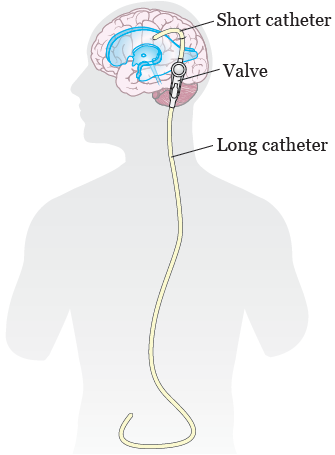
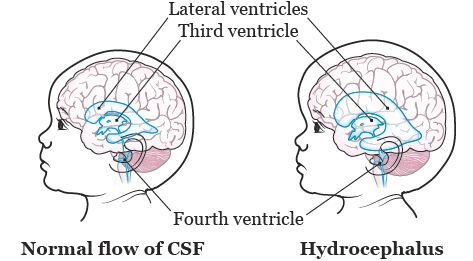
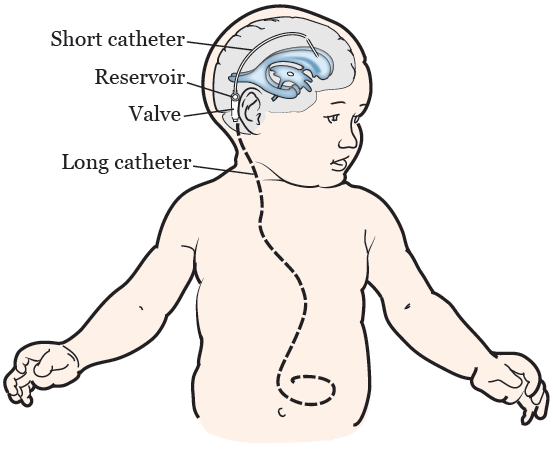
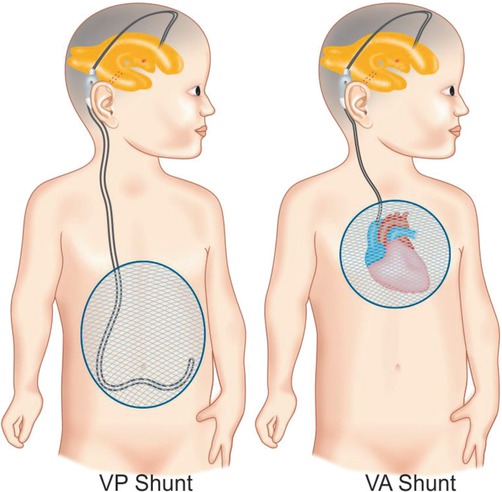
Vp shunt hearing loss. Hearing loss can be associated with a decrease in cerebrospinal fluid csf pressure because changes in csf pressure induce changes in perilymph pressure. Hearing loss after neurosurgical procedures have been reported but clinical information on hearing loss after the placement of ventriculoperitoneal vp shunts the most commonly used csf shunt for hydrocephalus patients is limited. This study is aimed to show the relationship between vp shunt and hearing loss.
Hearing loss after neurosurgical procedures have been reported but clinical information on hearing loss after the placement of ventriculoperitoneal vp shunts the most commonly used csf shunt for hydrocephalus patients is limited. Recovery of the hearing loss occurred 6 to 12 weeks after shunt placement in 75 of the ears examined. Study design prospective study.
2 5 to our knowledge this is the first case report of hydrocephalus associated snhl resolving after etv. Hearing loss after neurosurgical procedures have been reported but clinical information on hearing loss after the placement of ventriculoperitoneal vp shunts the most commonly used csf shunt for hydrocephalus patients is limited. Although the mechanism of snhl may vary based on the underlying etiology of hydrocephalus a direct relationship between intracranial pressure icp and hearing loss has been theorized.
The observation suggested v p shunt insufficiency can be clinically divided into two types one of which the chief symptom was marked hearing loss without dizziness and the other one of which is characterized by hearing loss without dizziness. Although shunt insertion for treatment of nph results in a decrease in hearing most of the loss can be recovered. 3 4 5 6 in 1 study 10 of 12 patients treated with vp shunt for hydrocephalus experienced a highfrequency cochlear hearing loss.
4 observed that 40 of ears of patients treated.