Vp Shunt General Anesthesia
The entire procedure takes about 90.
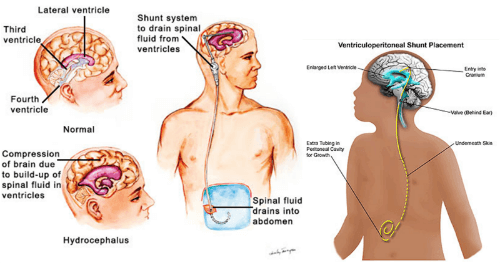
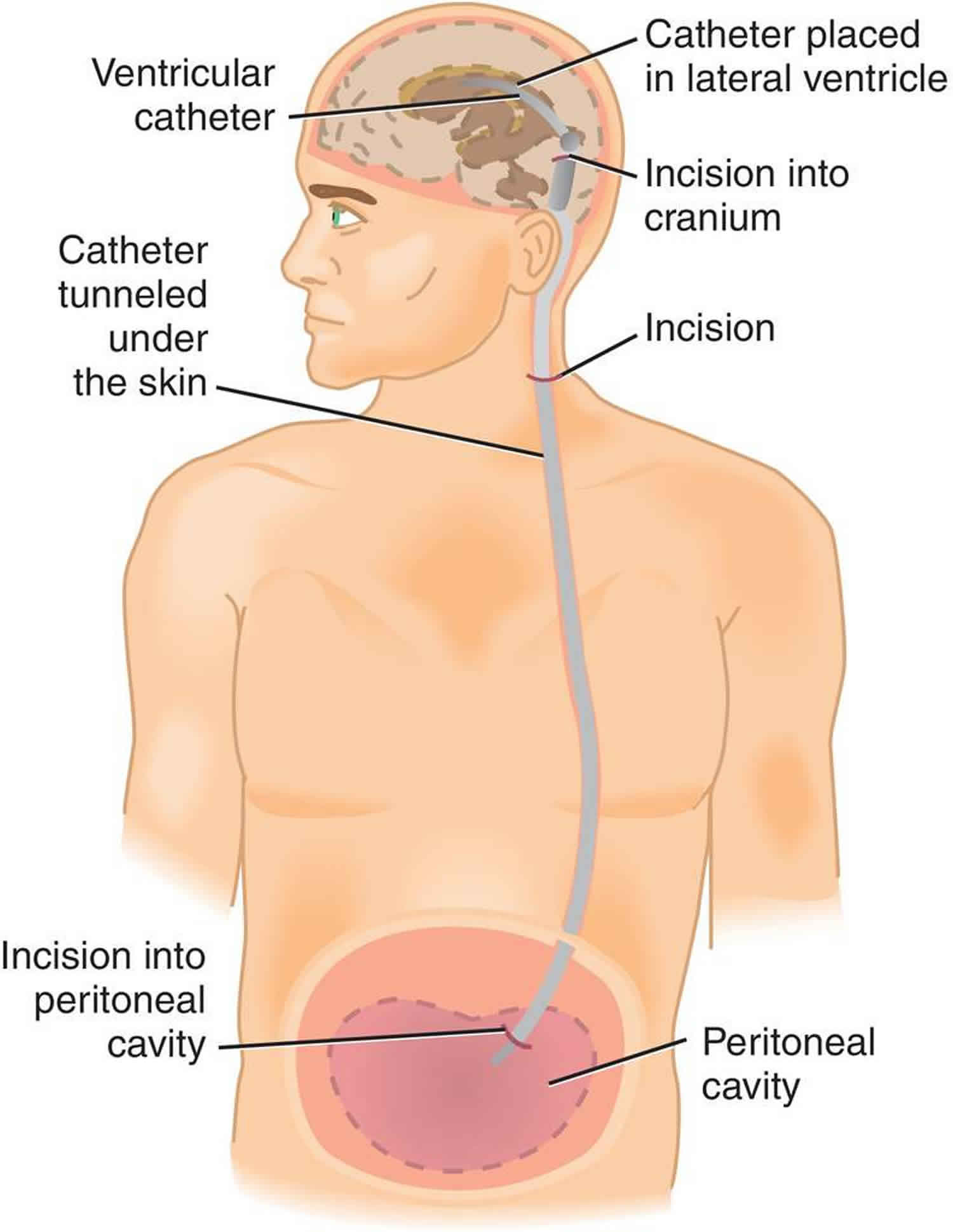
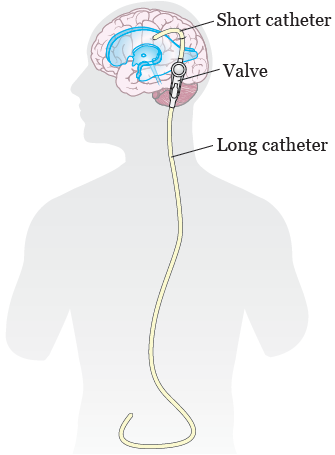
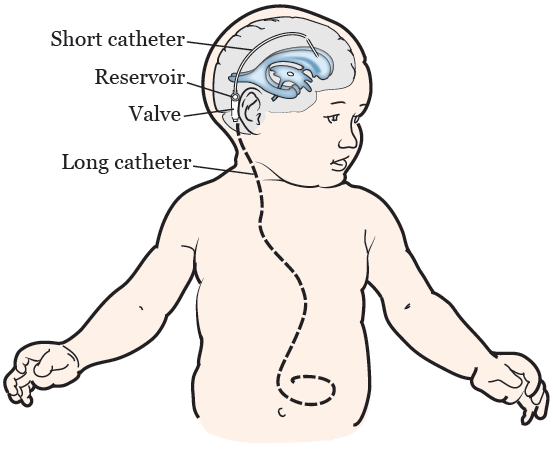
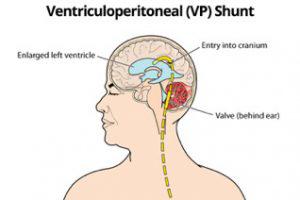
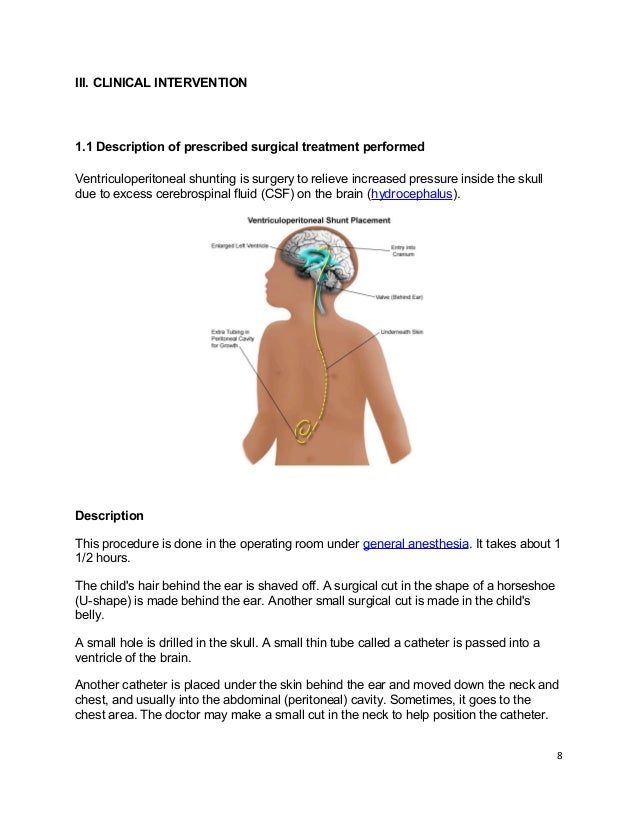
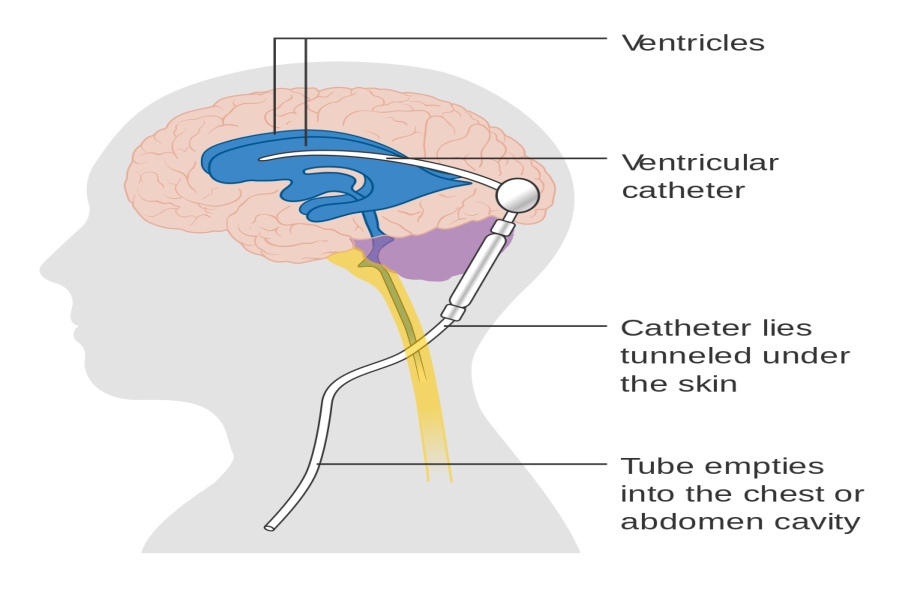
Vp shunt general anesthesia. The most common choice is a. Shunt system ventricular catheter peritoneal catheter and valve valve small medium or high pressure. Ventriculoperitoneal shunt placement or revision one of the most common pediatric neurosurgical.
Shunts often require replacement or revision making. The shunt provides a route for the csf to drain and decreases icp. You ll be asleep during the surgery and won t experience pain.
Rapid sequence intubation should be considered in patients with a recent history of nausea or vomiting. As with other cerebrospinal fluid csf shunt operations general anesthesia is administered. A vp shunt is placed in the operating room under general anesthesia by a neurosurgeon.
Gestation to consider analgesic options for labour and delivery and review anesthetic management in the event that an operative delivery was required. System to one of three places. Equipment needed to perform the procedure includes.
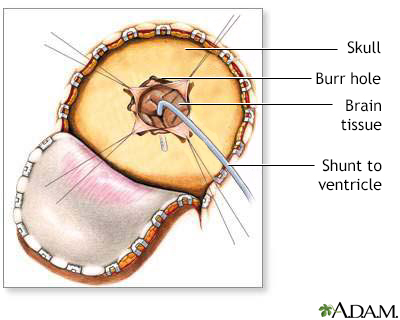
Erebrospinal fluid csf ascites is a very rare complication of ventriculoperitoneal vp shunt insertion and occurs as a result of inability of peritoneum to absorb csf. Doctors typically perform the placement of a vp shunt while a patient is under general anesthesia. As the child grows the.
Peritoneum atrium or the pleural cavity. There are several causes of hydrocephalus which may necessitate the insertion of a vp shunt see box 1. The anesthetist must assume that intracranial pressure icp may be elevated.