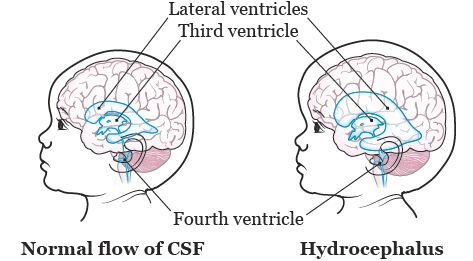
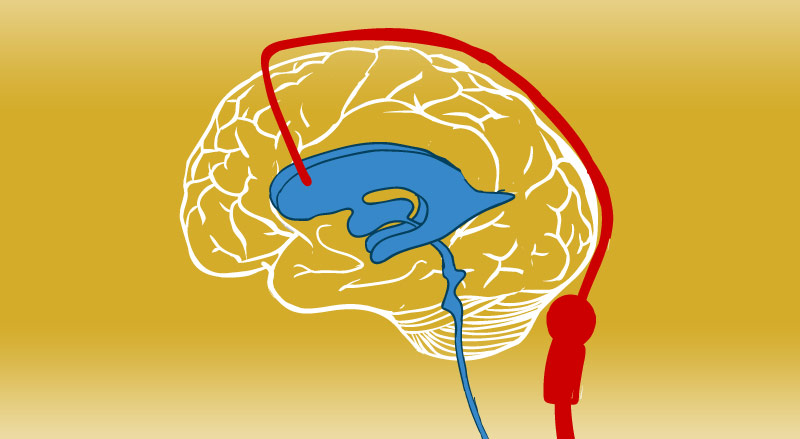
Vp Shunt Effect
Ventriculoperitoneal vp shunt complications include blockage and infection early and prompt detection of shunt dysfunction is vital as delay can lead to markedly raised intracranial pressure coning and death.
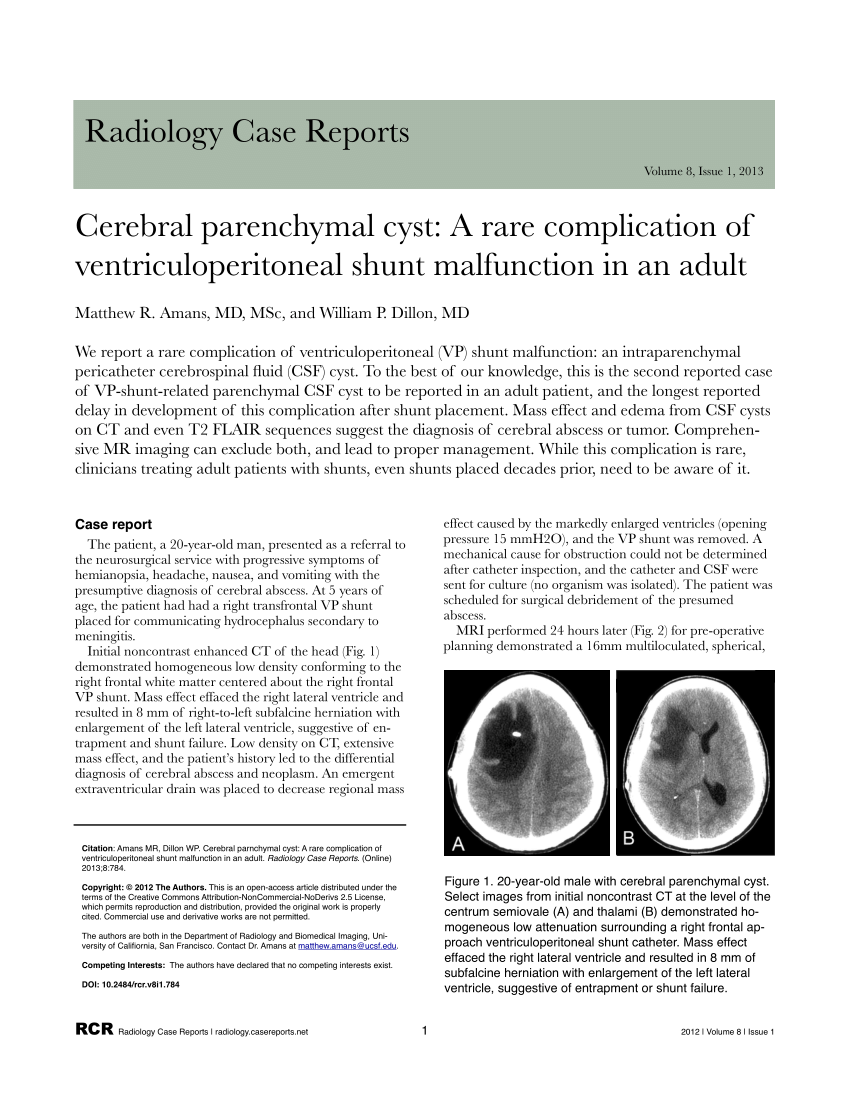
Vp shunt effect. Ap and lateral radiographs of the skull show a kink in the vp shunt in the middle of the neck. Ap and lateral radiographs of the skull shows migration of the vp shunt catheter tip out of its right sided burr hole in the skull. Axr above shows the tip of the vp shunt has migrated into the right scrotum.
There are a few different methods that can be used to relieve pressure around the brain. A ventriculoperitoneal shunt drains excess brain fluid reducing brain pressure to a safe level. Although obstruction and infection are the most common causes of shunt malfunction other complications can occur as well including bowel perforation pseudocyst formation and over draining which can lead to subdural hematoma formation.
The function of a vp shunt is to allow an escape route for this dangerous accumulation of fluid or blood. All patients with suspected vp shunt dysfunction should be discussed with neurosurgery. Ventriculoperitoneal shunts consist of a valve and two tubes called catheters which drain the.
A ventriculoperitoneal vp shunt is a medical device that relieves pressure on the brain caused by fluid accumulation.