Vp Shunt Complications In Adults
The remaining 43 patients for whom frontal vp shunt was done showed complications related to four patients only.
Vp shunt complications in adults. Swelling along shunt tract. Vp shunts were inserted for treatment of hydrocephalus. Although ventriculoperitoneal shunt vps surgery is the most frequent surgical treatment for patients with hydrocephalus modern rates of complications in adults are uncertain.
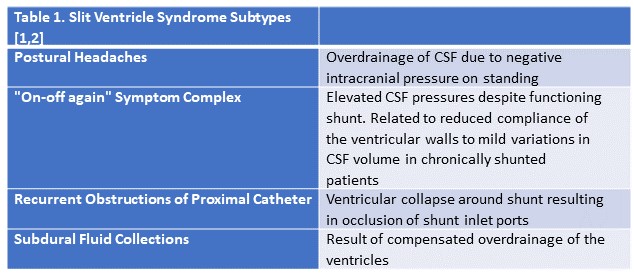
Mechanical complications shunt malfunction pain. Malfunctions can lead to serious complications such as over or under draining of csf. Protrusion of the catheter from the anus.
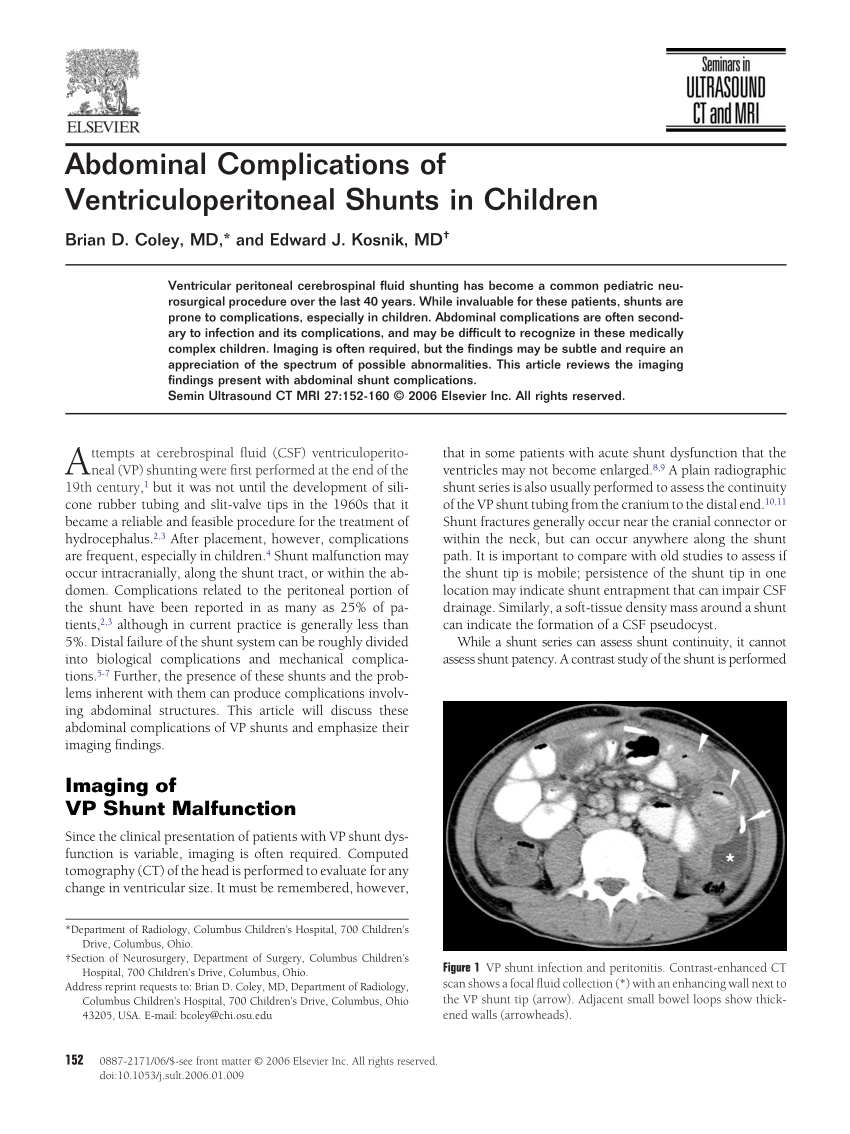
Shunt complications that develop in the peritoneum or abdominal area include peritoneal pseudocysts lost distal catheters bowel perforations and hernias. Fluid buildup can increase brain pressure which can be harmful. Redness along shunt tract potentially present with shunt failure or infection.
Abdominal injury ascites peritonitis abdominal perforations volvulus. Fever potentially present with shunt failure or infection. Although obstruction and infection are the most common causes of shunt malfunction other complications can occur as well including bowel perforation pseudocyst formation and over draining which can lead to subdural hematoma formation.
Methods we performed a retrospective cohort study of adult patients hospitalized at the time of their first recorded procedure code for vps surgery between 2005 and. Spontaneous knotting of the peritoneal catheter is a rare complication of the vp. Symptoms slowing of mental capacity unsteady on feet frequent falls incontinence drowsiness headaches less frequently.
Vp shunt was done. Signs papilloedema enlarged blind spots on visual field analysis or reduced visual acuity failure of upward gaze general clumsiness dyspraxic gait large head. Loss of coordination of balance.