Vp Shunt Complications Abdominal Pain

Surgery 79 188 192 1976 parry sw schuhmacher jf llewellyn rc.
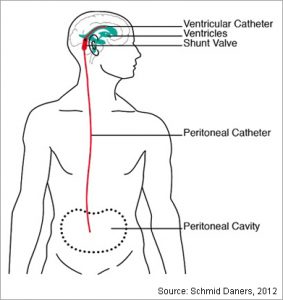
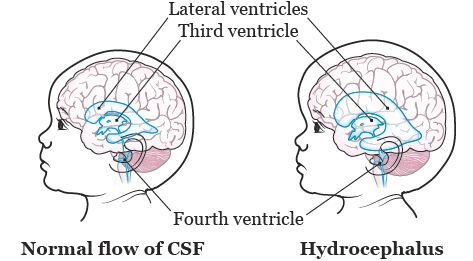
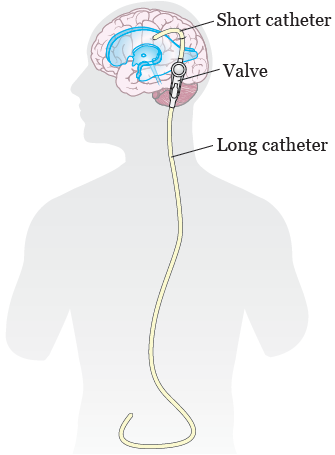
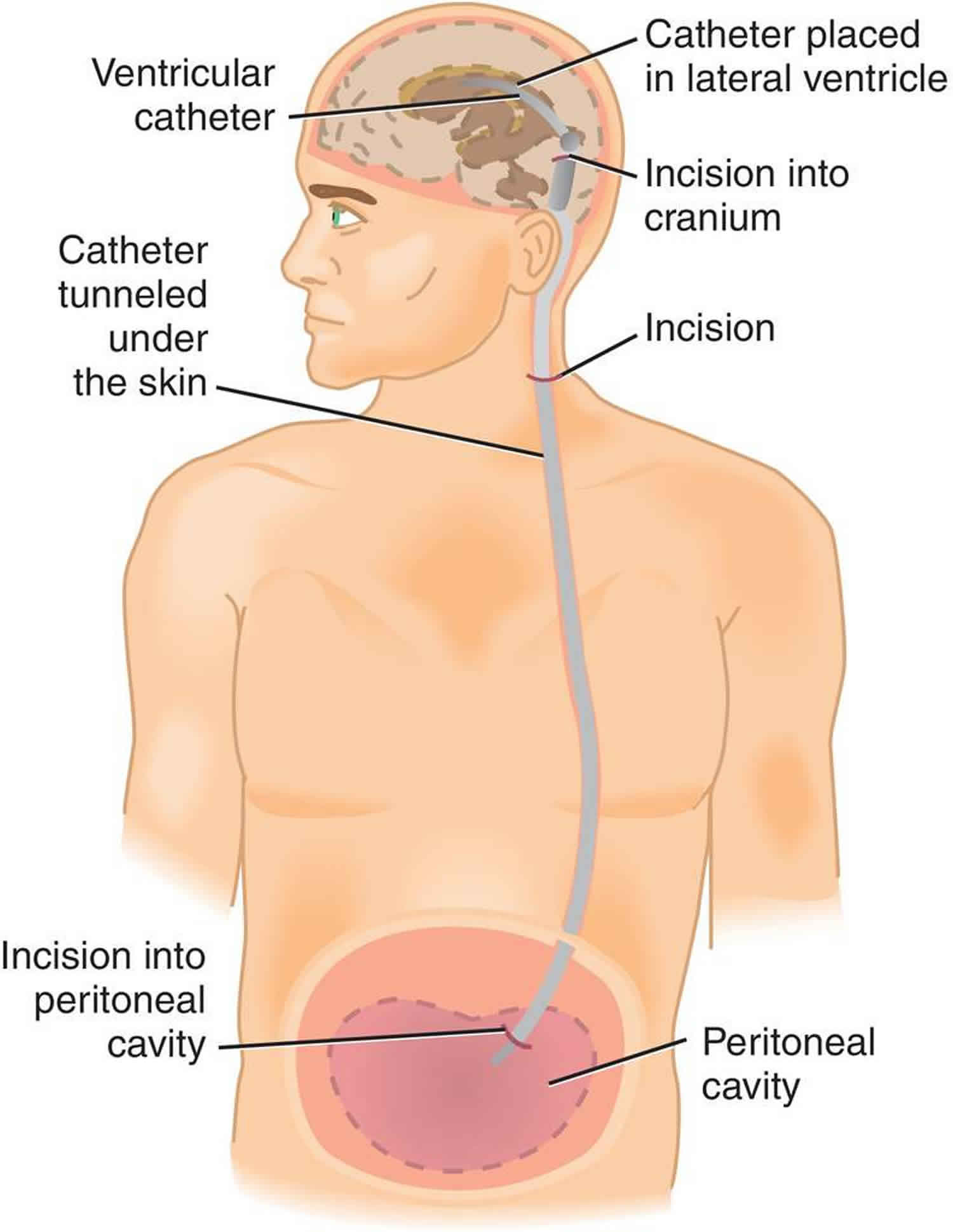
Vp shunt complications abdominal pain. Abdominal complications are reported in 5 47 of ventriculoperitoneal shunt cases 1 2. Persistent abdominal pain directly induced by a peritoneal catheter of a ventriculoperitoneal shunt which is associated with no other complications such as bowel perforation pseudocyst or infection has not been previously reported. Ventriculoperitoneal shunting is mainstay treatment of non obstructive hydrocephalus which deviates nature pathway of csf and drains into abdominal cavity.
In our study 16 patients 22 9 were histopathologically diagnosed with shunt related complications. A 65 year old woman with hydrocephalus developed persistent lower. Gutierrez fa raimondi aj.
Pseudocyst is a late complication of vps which may present as abdominal pain and a palpable mass. Although ventriculoperitoneal vp shunts do not have fewer complications than ventriculoatrial shunts the complications are less severe and have a lower mortality rate. The most common causes of shunt malfunction are catheter obstruction and infection.
Infection is the second most common cause of vps malfunction which is more common in children. Ventriculitis from shunt infection is a well documented complication of vp shunts and frequently occurs in the early postoperative period secondary to wound infection or intraoperative contamination. The peritoneum or abdominal area is the most popular site for distal catheter implantation.
Obstruction is the most common cause of ventriculoperitoneal shunt vps malfunction. The tip of distal catheter is usually placed in right lower quadrant. A complication of ventriculoperitoneal shunts.
The occurrance of a viscus. There are very rare reports of abdominal and pelvic pain directly induced by a vp shunt. Protrusion of the catheter from the anus.