Vp Shunt Blockage

The blockage is usually caused by chloroid plexus or blood generated during the placement of the catheter.
Vp shunt blockage. All patients with suspected vp shunt dysfunction should be discussed with neurosurgery. A shunt blockage from blood cells tissue or bacteria can occur in any part of the shunt. Any attempt to extract the tube should be performed with the aid of a neuroendoscope.
Death or major neurological sequelae including blindness are well described sequelae of delayed treatment. Shunt obstruction may occur proximally in the ventricular catheter as a result of choroid plexus red cells tumour cells or a high protein concentration in the csf. Pseudocyst formation is a common cause of distal catheter obstruction.
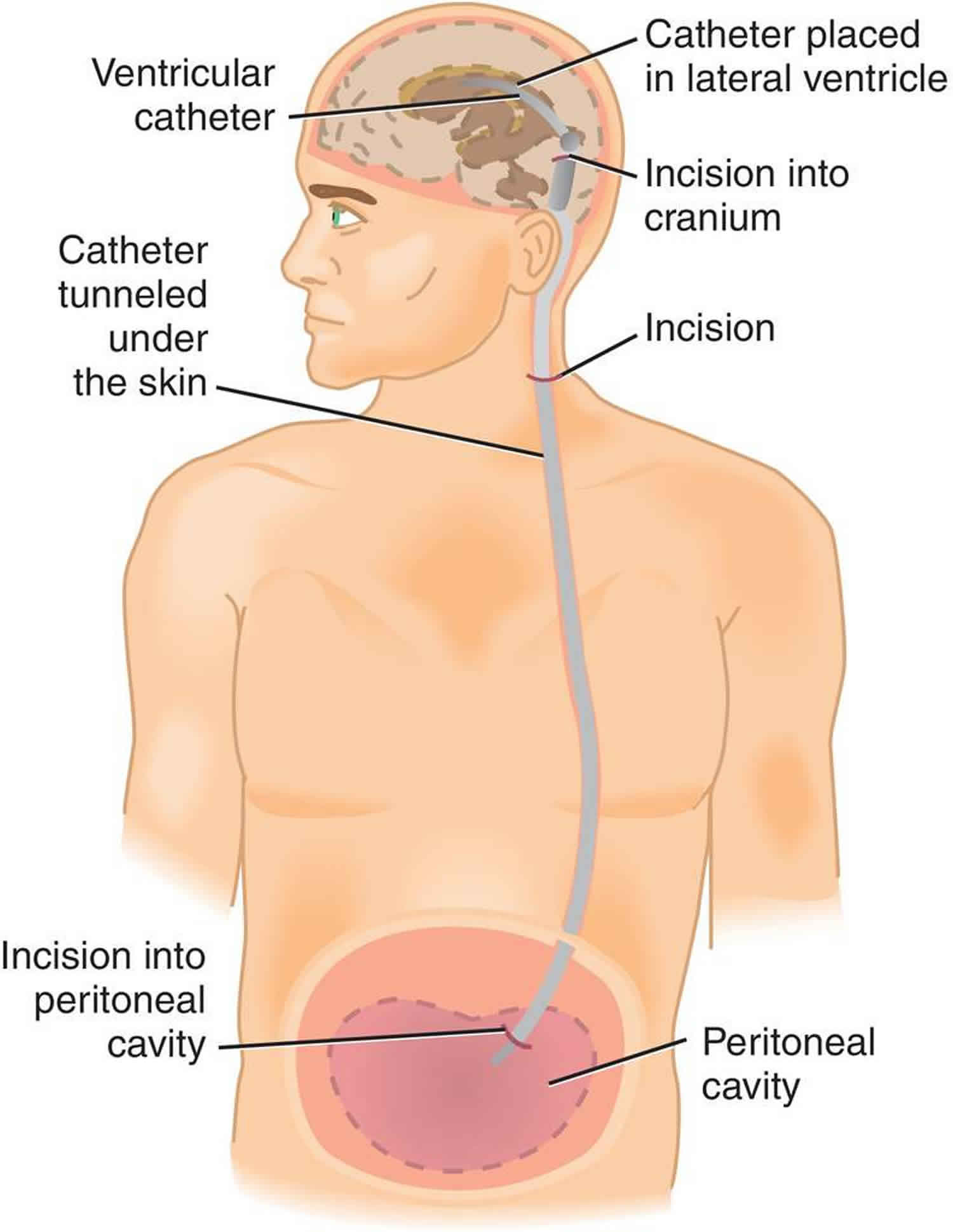
A ventriculoperitoneal shunt drains excess brain fluid reducing brain pressure to a safe level. Ventriculoperitoneal shunts consist of a valve and two tubes called catheters which drain the. Vps obstruction which is most often occurs in the proximal catheter is the most common cause of vps malfunction.
Hardware infection is the second most common cause of vps malfunction and this is a complication is. The proximal end the end within the ventricle of the brain is the most likely to be blocked. 5 difficulty in making the diagnosis may stem from a considerable symptom overlap with other common.
Value of the application of neuroendoscope in the treatment of ventriculoperitoneal shunt blockage neuroendoscopy techniques can be used to reveal the various causes of shunt obstruction. A ventriculoperitoneal vp shunt is a medical device that relieves pressure on the brain caused by fluid accumulation. Shunt malfunction may be attributed to multiple causes including obstruction infection pseudocyst formation and bowel perforation.
Blockage of the distal catheter can occur as a result of body growth if the shunt was placed during childhood adhesions within the abdominal cavity especially when associated with a low grade infection pregnancy and occasionally constipation. Vp shunting is a surgical procedure that primarily treats a condition called. In patients with ventriculoperitoneal shunts pseudocysts are caused by peritoneal adhesions or migration of the greater omentum over the shunt tip.